Principle of quartz crystal oscillator
1. The quartz crystal itself is a piezoelectric material, which generates an electric field on both sides of the crystal by applying an external voltage. Due to the mechanical and electrical coupling effect of the piezoelectric material itself, the crystal undergoes mechanical deformation, and the cutting surface of the crystal is subjected to mechanical stress, resulting in a potential difference between the two opposing sides of the crystal. This characteristic is called the piezoelectric effect. When we apply an AC voltage to the crystal, we can generate a cyclic oscillation of the chip; The frequency of oscillation varies depending on the crystal, and the thinner the quartz crystal cutting piece, the more difficult the cutting technique, but the higher the resonance frequency.
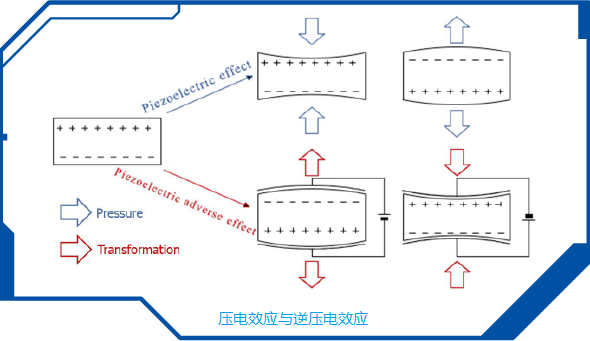
2. Piezoelectric effect of quartz crystal: When pressure is applied in the direction of the crystal axis, electrical changes occur on the quartz disk; On the contrary, when pressure is applied to the quartz disc, deformation and distortion occur inside the quartz crystal, known as the piezoelectric effect of the quartz crystal (as shown in the figure below). When subjected to force and deformation, polarization occurs internally, while opposite charges are generated on two surfaces. After the external force is removed, it returns to an uncharged state, which is called the piezoelectric effect. When the direction of force is changed, the polarity of the charge changes accordingly, and this phenomenon is called the "positive piezoelectric effect"; On the contrary, when an electric field is applied in the polarization direction of the dielectric, these electrolytes will also undergo geometric deformation, a phenomenon known as the "inverse piezoelectric effect".
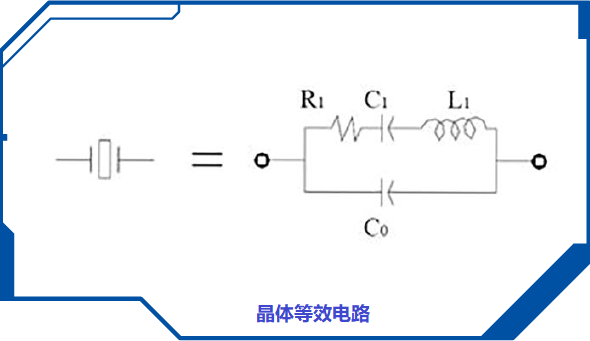
3. Crystal equivalent circuit: composed of dynamic capacitor C1, dynamic inductor L1, series resistor R1, and static capacitor C0. The following figure shows the equivalent circuit diagram of a quartz crystal to explain the basic elements that control the characteristics and performance of the crystal; The first three parameters are referred to as the "dynamic parameters" of quartz crystal components.